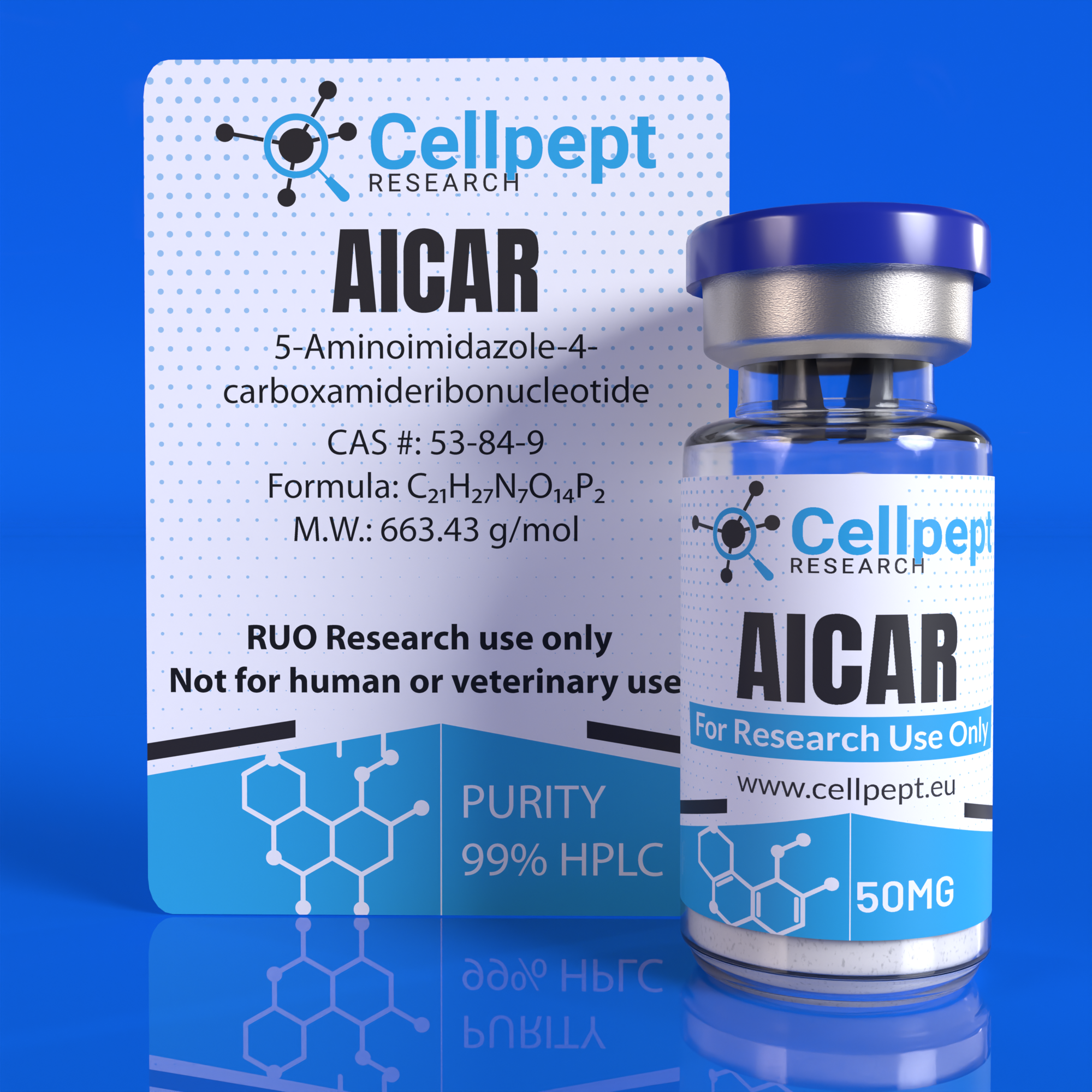
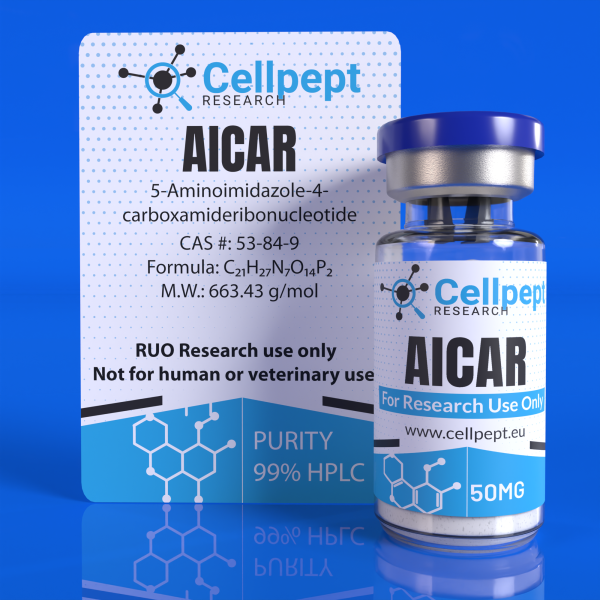
AICAR (5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide) is an analogue of adenosine monophosphate (AMP). It has been used clinically to protect against cardiac ischemia following heart attack. AICAR has antioxidant properties and may therefore help to slow the physiologic signs of aging. There is ongoing research into the use of AICAR to mediate the effects of diabetes, auto-immune diseases, and other inflammatory conditions. Both AICAR and AMP are thought to belong to a class of molecules called nucleotides, which serve as the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA. It is thought that nucleotides may play a key role in storing and transferring energy within cells. Because AICAR peptide mimics AMP, it may activate an enzyme called AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which is believed to help ensure that cells have the energy they need while limiting excessive energy storage. By stimulating AMPK, AICAR peptide is suggested to exert a wide range of relevant research implications when exposed to research models, such as:
- possibly supporting insulin resistance by making glucose more readily available to muscle cells
- potentially boosting the breakdown of stored energy, especially under conditions such as ischemia
- Believed to potentially reduce lipid accumulation inside various cells, such as liver cells
AICAR may also influence fatty acid oxidation, mitochondrial biogenesis, and the maintenance of slow-twitch, fatigue-resistant muscular tissue fibers, thereby influencing muscle cell endurance.
FOR RESEARCH ONLY
Exercise-mimetic AICAR transiently benefits brain function
AMPK agonist AICAR improves cognition and motor coordination in young and aged mice
AICAR stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis and BCAA catabolic enzyme expression in C2C12 myotubes

Reviews
Clear filtersThere are no reviews yet.